Von Willebrand Disease (VWD) is the most common hereditary bleeding disorder, affecting both men and women. Despite its prevalence, myths and uncertainties surround its management and impact on daily life. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify VWD, offering insights into effective treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and supportive care available through specialized centers like the Hemophilia Outreach Center (HOC) in Green Bay and Wausau.
Introduction to Von Willebrand Disease
Overview of VWD: Definition, Prevalence, and Types
VWD is an inherited bleeding disorder, meaning parents may pass the disorder on to their biological children 5. People with VWD have a problem with a protein in their blood called von Willebrand factor (VWF) that helps control bleeding 10. About 75% of people with VWD have Type 1 and may only need treatment if experiencing symptoms. Type 2 (including 2A, 2B, 2M, 2N) and Type 3 are more moderate to severe and often require treatment as both preventative and on-demand therapy.
Symptoms and Diagnosis: Common Signs, Diagnostic Tests, and the Importance of Early Detection
Common symptoms of VWD include frequent nosebleeds, bleeding for a long time after getting a minor cut, and for women, heavy menstrual bleeding 5. Early detection is crucial to manage the disease effectively and prevent complications. Genetic testing is not routinely performed in all countries, but it can be a valuable tool in diagnosing VWD 3.
Key Management Strategies for VWD
Living with VWD: Addressing the Challenges and Adjustments in Daily Activities
Living with VWD involves balancing daily activities with the need to prevent bleeding episodes. It’s important to know your limits and be prepared to handle accidents quickly 10. For example, certain over-the-counter medicines that can affect blood clotting, such as aspirin, ibuprofen, and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), should be avoided 2.
Von Willebrand Disease Treatment: Overview of Current Treatments, Including Medications and Therapies
The treatment for VWD often involves medications that help with blood clotting. Desmopressin, a synthetic hormone, is often the first treatment for managing VWD. It controls bleeding by stimulating the body to release more of the von Willebrand factor 1. In some cases, coagulation factor concentrates are used in nonresponsive individuals, in case of a contraindication for desmopressin, or in type 2B and type 3 VWD 3.
Emergency Care: Guidelines for Handling Bleeding Episodes and Injuries
In case of a bleeding episode or injury, it’s crucial to seek immediate medical attention. Your healthcare provider will guide you on the best course of action based on your specific type of VWD and the severity of your symptoms.
Lifestyle and Prevention
What Not to Do with VWD: Activities and Medications to Avoid
Certain activities and medications should be avoided to prevent bleeding episodes. For example, high-impact sports such as football, hockey, and wrestling may pose a risk of injury and subsequent bleeding 2. As mentioned earlier, certain over-the-counter medications that can affect blood clotting should also be avoided 2.
Diet for Von Willebrand Disease: Nutritional Recommendations and Foods that Can Help Manage Symptoms
While there’s no specific diet for VWD, maintaining a balanced and healthy diet can contribute to overall well-being and help manage symptoms. Iron supplements/iron replacement therapy may be recommended for those with anemia 6.
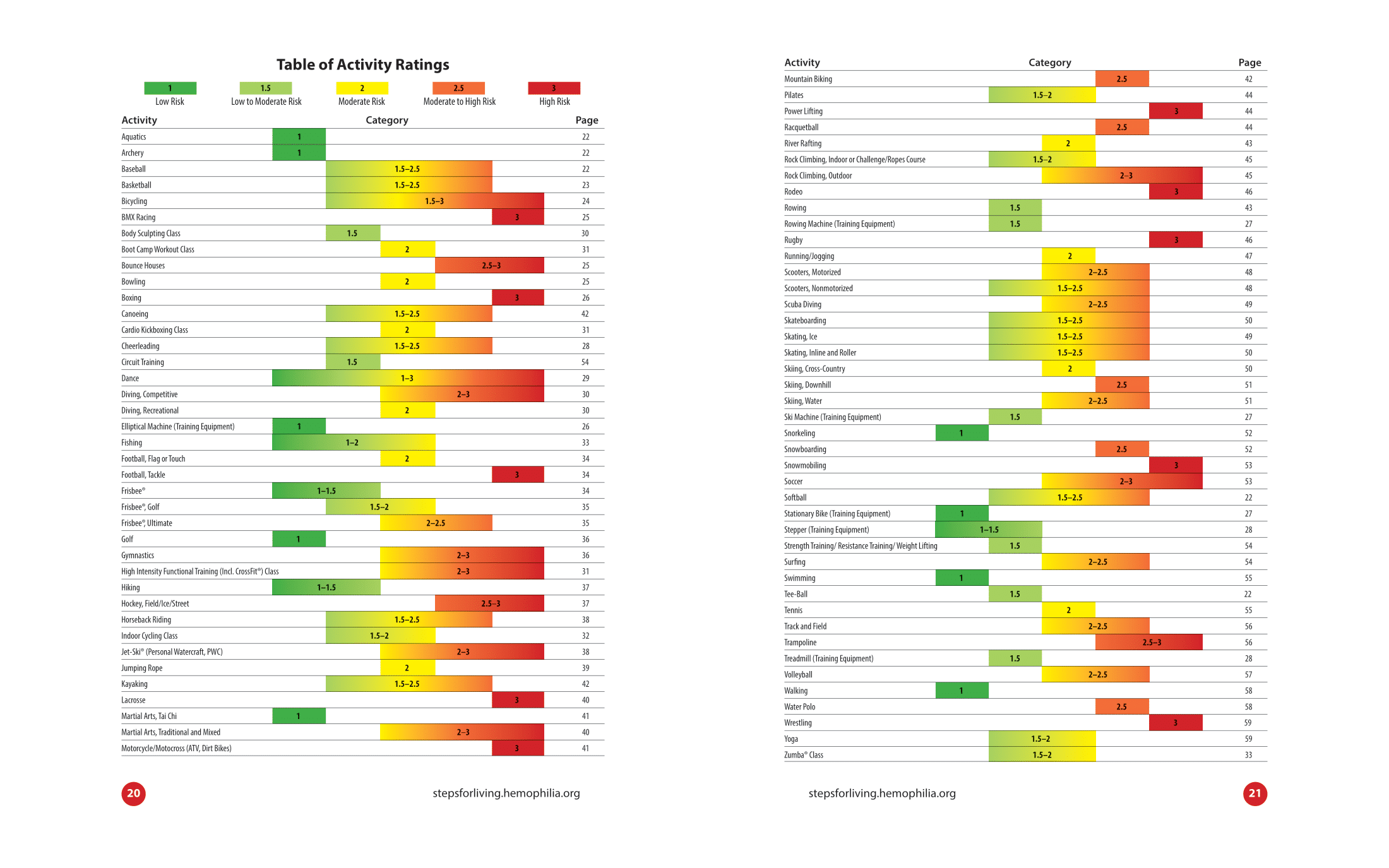
Exercise and VWD: Safe Physical Activities and Precautions
Physical activity is important for overall health, but it’s crucial to choose safe activities if you have VWD. Swimming, biking, and walking are generally safe activities. Always stretch before exercising and check with your doctor before starting any new exercise program 2.

Long-Term Outlook
Living a Normal Life with VWD: Strategies for Long-Term Management
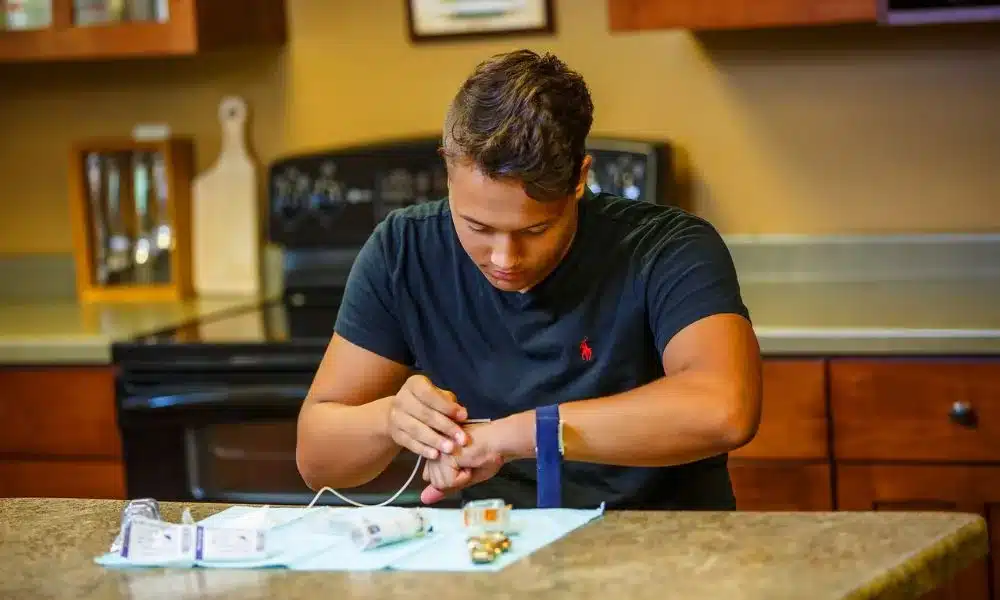
Despite the challenges posed by VWD, it’s possible to lead a normal life with the right management strategies. Regular check-ups with your Hemophilia treatment center, adherence to prescribed treatments, and lifestyle adjustments can help manage the disease effectively. It’s also important to educate family members about the disease, as they may also be at risk 2.
Innovations and Future Directions in VWD Treatment
The current treatments for VWD, including antifibrinolytics, desmopressin, and plasma-derived von Willebrand factor (pdVWF) replacement, have been around for decades. However, quality-of-life studies consistently demonstrate a significant mental and physical burden in patients, particularly in women 8. These emerging therapies offer hope for improved management of VWD in the future.

Specialized Care for VWD: Hemophilia Outreach Center (HOC)
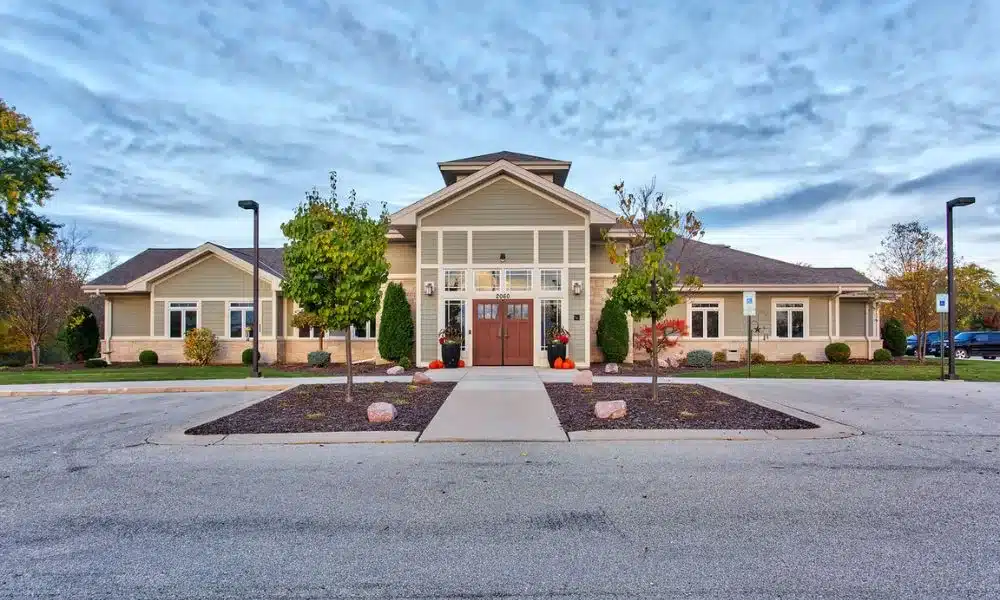
Hemophilia Outreach Center (HOC) plays a pivotal role in providing specialized care for individuals with VWD. With two treatment centers located in Green Bay and Wausau, HOC is dedicated to offering comprehensive support and treatment options tailored to the unique needs of each patient. These centers are staffed by experienced healthcare professionals who specialize in bleeding disorders, ensuring that patients receive the highest quality of care.
The presence of two locations allows for greater accessibility for patients across the region, making it easier for them to receive the care they need. HOC’s commitment to patient education, advocacy, and innovative treatment approaches underscores its importance in the VWD community. By fostering a collaborative care model, HOC ensures that patients and their families are equipped with the knowledge and resources necessary to manage VWD effectively, enhancing their quality of life.




